Found 2 results
Article
14 May 2024Measurement and Structure of Common Prosperity of Urban Residents the Case of Hangzhou, China
Common prosperity is an important feature of the social state that the people of the world aspire to, and an important feature of the Chinese path to modernization. Taking common prosperity as the result of income and assets does not facilitate a full understanding of people’s common prosperity, because common prosperity also includes people’s pursuit of subjective happiness such as happiness and satisfaction. From the perspective of the need for a better life in China, this study constructs a subjective evaluation system of the common prosperity of urban residents, including 5 dimensions and 25 specific indicators. It uses survey data from 460 participants and applies the graded response models to estimate parameters and predict latent variables. We find that 21 indicators are in line with the reasonable range of basic assumptions and parameters. They have a strong ability to distinguish the common prosperity of residents in different regions, but have different functional characteristics. The confirmatory factor analysis shows that the common prosperity index of residents includes four potential factors: income, education, medical care, and old-age care, and ecology, which has a good structural effect. In terms of weight, education, medical care and old-age care are the most important factors influencing common prosperity. Among them, the classification policy of high school entrance examination, the quality and fairness of primary and secondary education, the degree of medical insurance security, and the waste sorting and community security are important aspects of evaluating the Common prosperity of residents.
Article
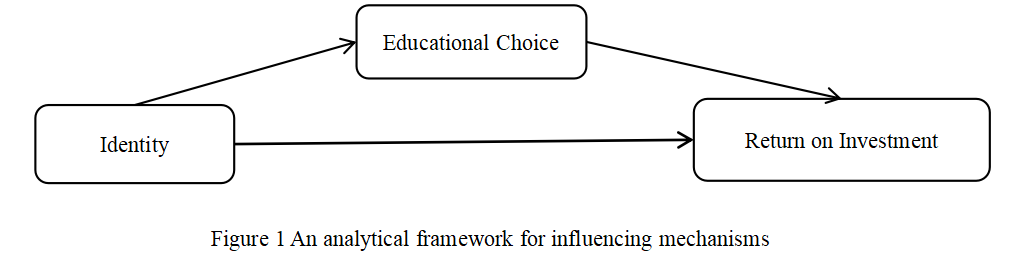
01 April 2024Identity, Secondary Vocational Education Options and Return on Investment: Evidence from Children of Rural Chinese Families
With the continuous improvement of living standards, the importance of educational choice becomes more and more prominent. Based on the data of China General Social Survey (CGSS), a simultaneous equation model of identity, secondary vocational education choice and investment return is constructed. On the basis of fully considering endogeneity and sample selection bias, this paper analyzes the influence of identity on secondary vocational education choice and investment return by means of instrumental variables and propensity score matching (PSM). It is found that class differentiation is the main factor affecting class identity. The more blurred class differentiation, the higher class identity. Class identity has a significant positive impact on identity. The higher class identity, the easier it is to form identity. Identity has a direct positive impact on personal investment return. The stronger the identity, the higher the investment return. At the same time, identity has a significant positive impact on the choice of secondary vocational education. The stronger the identity, the more inclined to choose secondary vocational education. Compared with individuals with junior high school education, individuals with secondary vocational education have a higher return on education investment. Therefore, identity can not only directly improve an individual’s return on investment, but also improve the possibility of an individual’s choice of secondary vocational education, thereby improving an individual’s return on education investment, and ultimately increasing an individual’s return on investment.